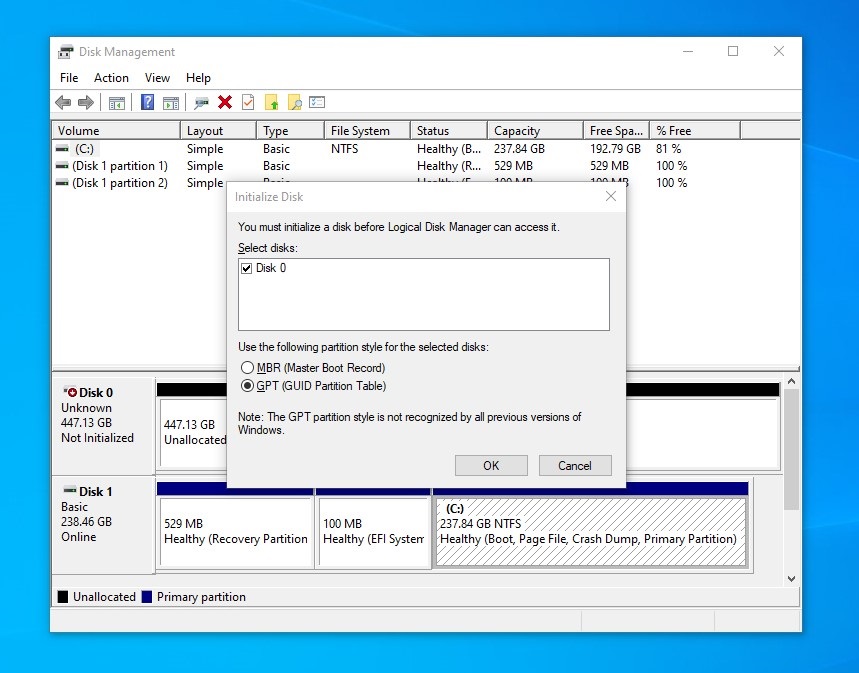
When you plug in a newly-purchased HDD or SDD to the computer, the operating system will often ask you to initialize the disk. Have you ever wondered what the differences between MBR and GPT? Which partition style should you choose?
What are MBR and GPT?
MBR (Master Boot Record) and GPT (GUID Partition Table) are the formats to store all the partitioning information for the drives. They allow for the OS to recognize and boot from the existing partitions. Users will have to decide to use MBR or GPT during initialization, prior to creating any partitions.
MBR is first introduced by IBM in 1983 on their PC DOS 2.0 system. Just as its name implies, it is a special partition in the drive, containing a boot loader and partitioning data. The operating system will need to execute the code in the MBR to correctly start, after the BIOS is posted. This is why Windows will sometimes fail to start, when the MBR is corrupted.
GPT is developed as a replacement of the aging MBR format, which is also part of the UEFI (Unified Extensible Firmware Interface) standard. Every partition in a GPT drive is given a universally unique identifiers or globally unique identifiers (GUIDs).
Comparison – MBR vs GPT
Storage Capacity
At the time when MBR is launched, hard drives of several terabytes (TB) are insanely and impossibly large. The tiny 512-byte sector of the MBR limits it from allocating disks with more than 2.2 TB of space. In contrast, GPT with 64-bit addressing can work with drives up to 18 Exabytes (EB) of capacity. For your reference, 1 EB equals to 1024 Petabytes (PB) or 1048576 TB.
Number of Partitions
Apart from restricted capacity, MBR-based drives can only create four primary partitions on a single disk. Although you can increase the number by modifying an existing partition to a extended partition, it takes unnecessarily complicated steps to achieve. GPT, on the other hand, supports a maximum of 128 partitions in Windows, which is way more than enough for most users.
Reliability and Security
Unlike MBR, GPT creates and stores multiple copies of the boot loader and partitioning information in the disk. It is harder to affect the whole operating system and can be easily recovered, if some of the code are overwritten or corrupted. GPT also has a primary and a backup partition table with cyclic redundancy check (CRC) implemented for better data integrity.
Compatibility
Newer UEFI-based system should be compatible with both MBR and GPT, while legacy BIOS can only work with MBR. All 64-bit Windows 7 to Windows 10 and their Windows Server versions supports using GPT disks for booting and data with UEFI.
We recommend users to use GPT on their new drives, if possible. It is a more modern and reliable standard, which provides various advantages over MBR.
Feel free to leave comments below. Share the article if you enjoy reading it. Follow us on Twitter, Facebook, Instagram and Pinterest.
Support this website simply by shopping on Amazon and Newegg. We will receive small kickbacks, if the above affiliate links are used to make any purchases.
















How many operating systems can be installed on a single system beside Windows 10